
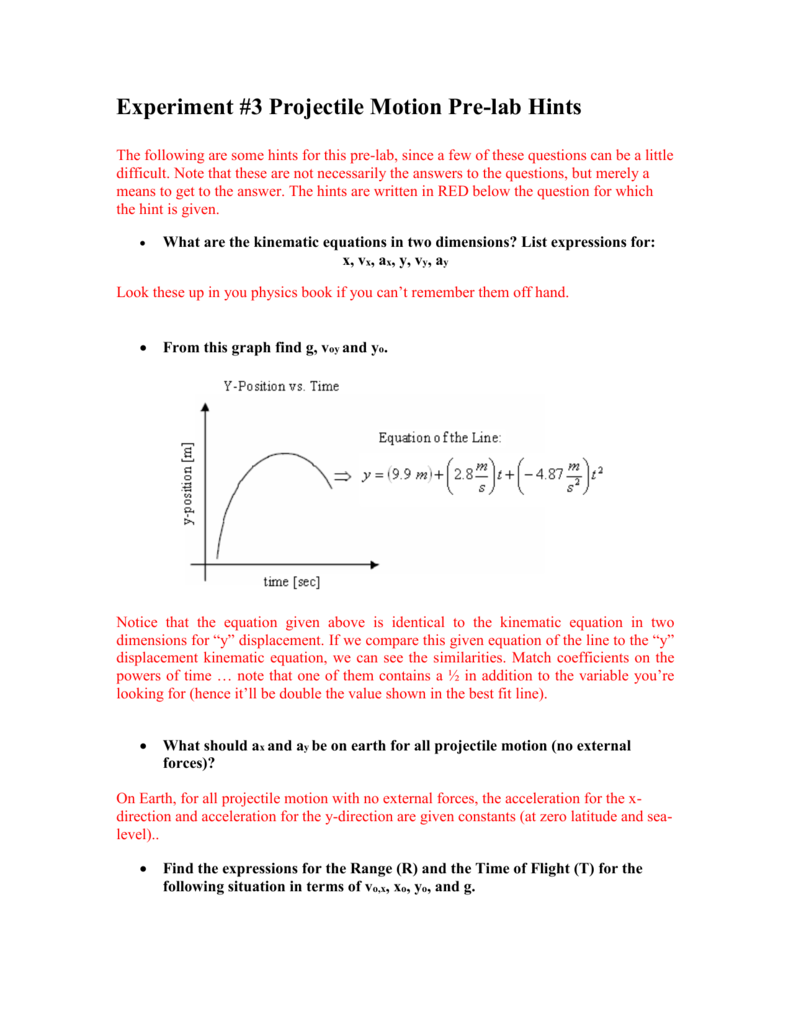
The key to analyzing two-dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions, one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical.
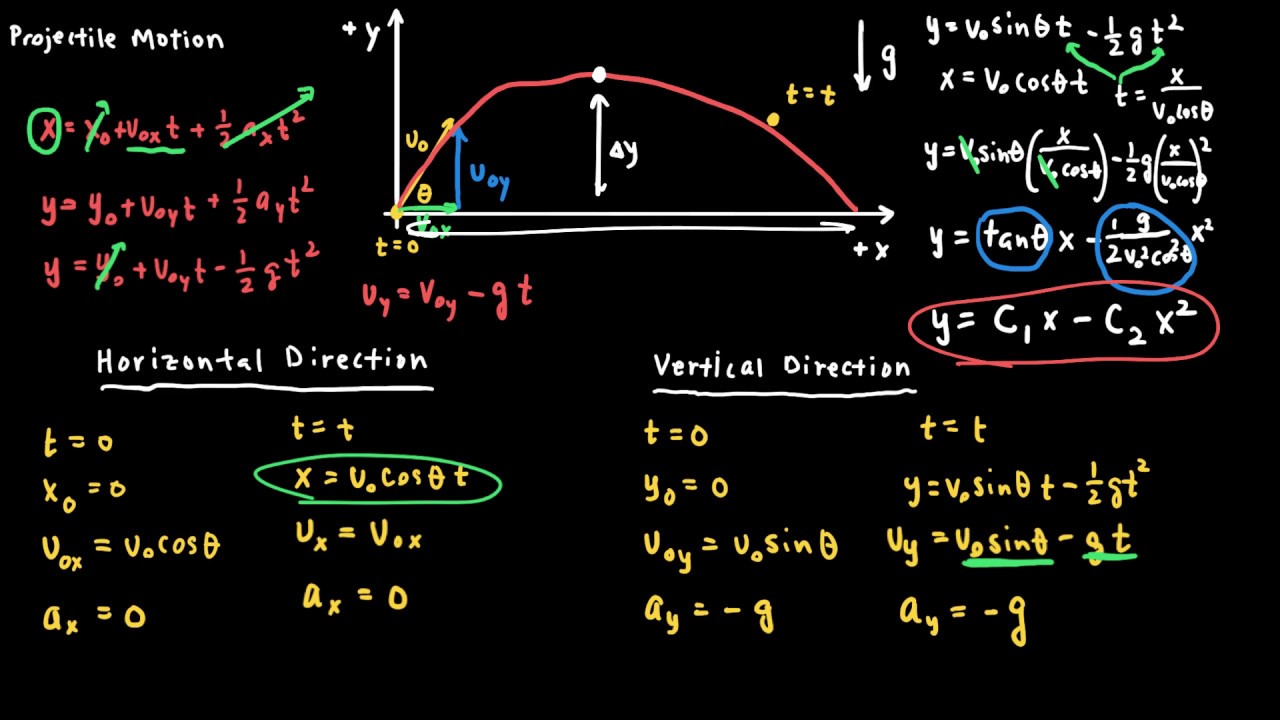
This fact was discussed in Kinematics in Two Dimensions: An Introduction, where vertical and horizontal motions were seen to be independent. The most important fact to remember here is that motions along perpendicular axes are independent and thus can be analyzed separately. In this section, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, such as that of a football or other object for which air resistance is negligible. The motion of falling objects, as covered in Problem-Solving Basics for One-Dimensional Kinematics, is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is no horizontal movement. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory. Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. Apply the principle of independence of motion to solve projectile motion problems.Determine the location and velocity of a projectile at different points in its trajectory.Identify and explain the properties of a projectile, such as acceleration due to gravity, range, maximum height, and trajectory.The range (R) of an object in projectile motion is defined as the distance from the point of projection to the point at which the particle reaches the ground again.The horizontal component of the motion is at a constant velocity, while the vertical motion is subject to a constant acceleration due to gravity (g). The motion of projectiles is analysed in terms of two independent motions at right angles.Projectile motion of any object is a parabola.Projectile motion is the two-dimensional motion of an object due to the external force and gravity.Applying this value in horizontal component of the motion, the horizontal distance travelled can be calculated. Now, it is known that the ball travels for 4 seconds before reaching the ground.

How long does it take to reach the ground? How far from the base of the building is it when it reaches the ground?

The range (R) can be calculated using the formula:Ī ball is thrown from the top of a building, 45 m high above ground level, with an initial velocity of 15 m s-1 in a horizontal direction ( Figure: 4). If a particle projected with velocity (u) at an angle (Ө) to the horizontal from a point on level ground, the range (R) is defined as the distance from the point of projection to the point at which the particle reaches the ground again. The combination of horizontal force and gravitational force tends to move the object in a parabolic path, as illustrated in the following drawing. The horizontal force acting on the object tends to move the object horizontally and the gravitational force acting on the object tends to move the object downwards. Figure 2 explains a scenario where projectile motion happens. The projectile motion of a particle can be studied by splitting the motion into horizontal and vertical components, and considering the forces that move the object separately. The curve traced out by the object subject to a constant force in one direction is a parabola. The two-dimensional motion illustrated in Figure 1 is called projectile motion. In this article, the concept of two-dimensional motion and the equations that govern the two-dimensional motion are explained. The motion of the ball is two-dimensional, as illustrated in Figure 1. Now, consider a ball kicked by a football player. The motion of the car is one-dimensional. Consider a car that is moving in a straight line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
